
Startups provide unique solutions to the problems facing society, or to be more precise; offer unfamiliar solutions to familiar problems, which means that each startup relies on an uncommon private idea and represents a unique model itself; but most startups are in common with what is known as The Startup Lifecycle, which means the stages that the company goes through, starting from Idea and establishment, leading to growth and expansion.
Why should an entrepreneur recognize The Startups Lifecycle and understand their stages accurately?
If you are an entrepreneur, and you have an idea that you think you can penetrate the market through and intend to launch your startup based on that, you should prepare to go through many phases in which you will face difficulties and challenges. You may find remarkable progress in some of them, but these phases are known to experts as the typical situation that any startup goes through.
Accordingly, any entrepreneur thinking of launching his startup must know these stages and try to understand them thoroughly so that he can face and overcome the challenges he experiences at these stages brilliantly. He also must take advantage of the ascent points in the startup lifecycle and the opportunities available to him.
What are the startup lifecycle stages?
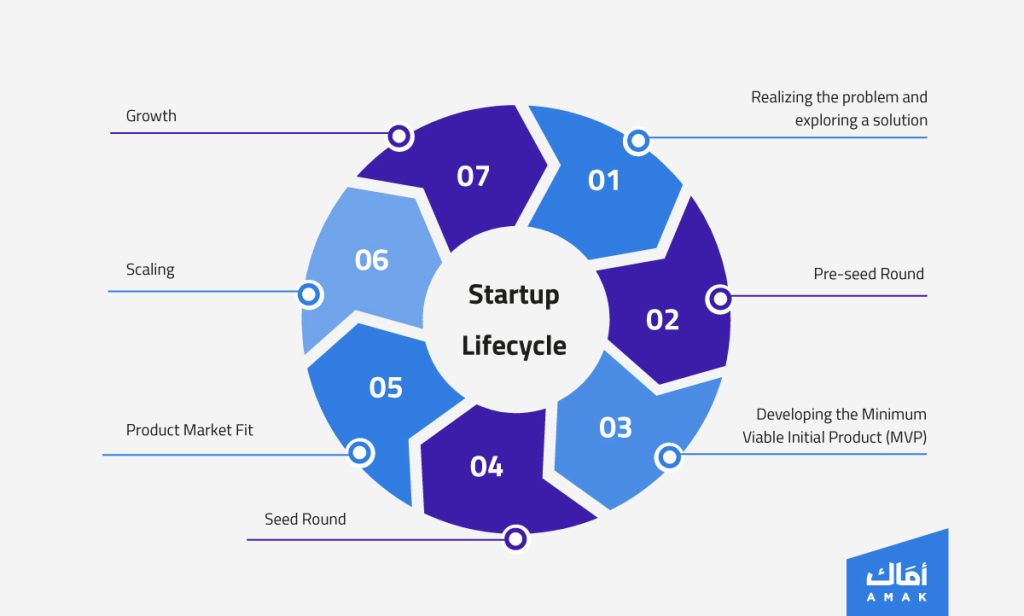
Experts’ opinions vary in the number of startup lifecycle phases. Some believe this cycle is limited to three stages, starting with the idea, launching and testing the product, and ending with growth and expansion. However, most entrepreneurship experts believe that startups typically go through five stages, which can be analyzed extensively to include seven primary stages suitable for all types of startups in general. These stages, in order, are:
- Realizing the problem and exploring a solution
- Pre-seed Round
- Developing The Minimum Viable Initial Product (MVP)
- The Seed Round
- The Product Market Fit
- Scaling
- Maturity and Growth
In the following paragraphs, we will discuss each of these stages separately, in addition to the things an entrepreneur must do at each stage, the challenges he faces and how to overcome them.
1- Realizing the problem and exploring a solution
This phase is the cornerstone of any startup because all upcoming stages depend mainly on it. At this phase, the entrepreneur aims to look for a problem in a segment of society and devise an appropriate solution. To find the required idea, he must ascertain that the problem he wants to solve is facing a specific group of people and that this group really needs this solution. He must also ensure that the solution he has reached is truly appropriate to this problem.
The most common mistake at this stage is launching the startup with a prior assumption that a specific group in society will definitely buy the service or product you provide. Therefore, some necessary steps must be followed to avoid falling into this problem, including:
- Define your target audience accurately, get to know your target customers closely, be passionate about communicating with them and ascertaining their needs, try to meet some of them personally, and be sure to read customer comments on social media that relate to the problem you want to solve.
- Define the pain of your customers: Customer pain can be defined as the need to confirm that your product is valuable to customers.
- Ask your customers about the solutions they used previously for the same problem. Then, try to benefit from that with feedback to develop your idea and make appropriate modifications.
- Try to finalize the idea to become ready for implementation, adapting to customers’ opinions and pains.
This stage requires great accuracy of observing while communicating with the target audience and a superior ability to access all customer information which can be critical while developing the needed solution to the existing problem.
2- Pre-seed Round
Some startups skip this stage if the idea of the product they want to develop requires only minimal expenses. But most entrepreneurs often need to go through this stage, which for them means risking many things in their lives, such as a job and some money and savings they have.
This stage does not mean that financing is not needed; instead, it means trying to finance the idea subjectively because investors only finance companies on the ground whose data reflects the results achieved, as they do not pay for ideas only.
Some solutions to skip this stage
- 1. Dependence on personal and family financial savings.
- 2. Obtaining a loan from the bank to finance the initial product launch.
- 3. Joining business competitions launched by business incubators. Some of these incubators give financial rewards to entrepreneurs who successfully pass the early stages of the competition.
3- Developing The Minimum Viable Initial Product (MVP)
Many entrepreneurs make big mistakes when they assume their idea is successful and a segment of customers are ready to buy their product. They launch their product without any testing, and their projects fail in their infancy! After passing the previous two stages, the entrepreneur should develop what is known as the minimum viable product (MVP), which means a simple prototype that represents the idea of the entrepreneur and the solutions he offers, such as a very simple front mobile application, or selling a product through a mobile cart instead of selling it in a shop.
This means that building the MVP model must be done with the lowest possible investment of time and capital to ensure the idea is acceptable, identify customers’ behaviour towards it, and minimize risks to the lowest possible level. Therefore, customer engagement in the details of each stage of product development is crucial in developing it properly. The following are the most critical steps that can be followed to know customer opinions and expectations of the product:
- Personal interviews with the initial segment of target customers and obtaining their opinions about the MVP and its suitability for their needs.
- Conducting an A / B test that helps compare two variables, that is, comparing two product versions to adopt the best version for customers.
- Using social media to find customer opinions through their comments and discussions about the product and alternative products.
Keep in mind that building the MVP model takes time that varies from company to company. This stage requires deliberation and patience for some companies during product development and modification. It may take a long time to reach an acceptable product version.
4- Seed Round
After the successful development of the MVP, startups move to the seed round funding stage, called the Seed Round. This stage is like planting the project’s seeds and watering them until they grow into a tree. Seed funding helps entrepreneurs secure the first steps of their company, such as funding market research, product development, and hiring an initial staff to pursue new tasks.
Many potential investors, such as business incubators and venture capital firms, are at this stage. Still, the most important and common types of investors in the initial financing stage are known as (Angel Investors.), this type of investor tends to finance a group of high-risk projects to gain a significant share in these projects if any of them succeed.
During this funding round, the entrepreneur must prove the initial success of his idea in its prototype through data and statistics confirming customers’ interest in the product, its achievement of sufficient revenues, and its readiness to move to a higher level.
The main benefits of the Seed Round
- Saves more time for product development by funding the tools to do so.
- leads to great flexibility in making appropriate adjustments to market demand.
- Reflects positively on the startup’s reputation in the market.
5- Product Market Fit
After obtaining the initial financing, the entrepreneur needs to develop his product to a higher level than the initial one to become more suitable for the market and achieve a higher ability to compete and meet the needs of a larger group of customers or new categories such as well. At this stage, the startup makes qualitative leaps and rapid growth.
The following questions help determine how sophisticated the product can become:
- Is there interest from potential customers in using your product?
- Have they come to prefer your product to that of your competitors?
- Do customers recognize the added value in your product?
You can determine the volume of development required in the product after answering the previous questions; then, the product development process begins by making a set of improvements, removing unnecessary elements from the product, and enhancing effective parts that represent a unique value for customers.
Many entrepreneurs make a big mistake at this stage of spending available resources for development in all directions. Therefore, at this stage, the focus should be on developing in a specific direction and choosing which direction is the most important for the most effective customer channels, then moving to develop other directions after reaching what suits the market in this direction.
6- Scaling
The expansion of work is a response to the company’s stalling growth and reaching a steady level of sales, so the entrepreneur should look for the best methods and practices to expand and develop the scope of work. The most important of these methods are:
- Employing a team of experts in sensitive departments of the company.
- Outsourcing some business to external companies to accomplish it more efficiently.
- Dealing with a larger group of suppliers and companies related to the field of work.
- Searching for more investment opportunities and building partnerships.
Expanding the work team is the best procedure at this stage. The presence of qualified employees leads to growth and expansion, whether by developing existing products or introducing new products for the company. Perhaps the most common mistake at this stage is the belief that the difficult stages of the company’s life have ended and that there are no more challenges ahead, so we must stay focused and persistent in the business and pay more attention to the internal affairs of the company.
7- Maturity and Growth
Many startups may not reach this stage, and some stop at a steady growth limit that they do not exceed, but this phase is crucial for companies that have successfully passed previous stages, and their owners are looking for entirely new markets, seeking to increase the size of their companies and being in different geographical locations. At this stage, the entrepreneur must search for more growth opportunities, and this is done through developing existing products and adding new value to them or by building new products to solve different problems.
But the most common procedure for companies that reach this stage is to search for acquisition offers by large companies that can move the startup to advanced levels, new markets, and different countries. The experiences of startups that have moved to regional and global markets indicate that the most to avoid at this stage are to stay in the current market, as the primary objective of this phase is to expand new markets in different countries from the entrepreneur’s country and to face new challenges in these countries.
In conclusion, focusing and working passionately is the common link at all previous stages. Therefore, it is necessary to give each stage its due amount of work and time, and all the turns between these stages, which could lead to the company’s failure, must be carefully treated.
Finally, business incubators, through the competitions they launch, provide a unique opportunity for entrepreneurs to bypass these stages and overcome the existing challenges with the least time and effort through the training programs they implement, the financial rewards they give to distinguished entrepreneurs, in addition to experts and mentors who accompany startups during the establishment period. Business incubators also provide networking opportunities with relevant projects and potential investors for greater funding opportunities.